What is Phenylketonuria (PKU)?
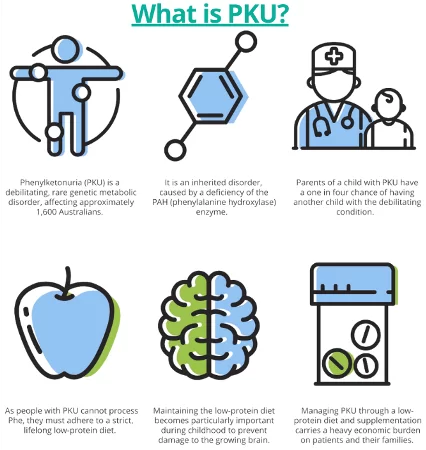
Phenylketonuria – or PKU – is a rare, inherited metabolic disorder. It effects 1 in 10,000, babies born in Australia. Individuals with PKU are unable to effectively break down the amino acid Phenylalanine (Phe) in protein. If a person with PKU eats too much protein in their diet the level of Phe can build up to dangerous levels which can lead to:
- Neurological complications
- Behavioural and emotional issues
- Liver problems and other conditions
- In some cases, brain damage
PKU is a manageable condition, and with strict, lifelong dietary management individuals are able to lead a life full of potential.
Definition
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an autosomal recessive inherited disorder caused by the genetic mutation of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), which converts the essential amino acid phenylalanine into tyrosine. If its function is disrupted, an accumulation of toxic metabolic products occurs. This can result in severe neurological damage if left untreated. For a child to inherit PKU, both parents must carry the faulty gene.
Phenylketonuria Diagnosis
PKU is diagnosed through the Newborn Bloodspot screening program – available to all babies born in Australia 48-72 hours after birth. If the screening test reveals an abnormal result, healthcare providers will contact you and arrange for further testing to confirm a diagnosis for your baby. If the diagnosis confirms PKU, a metabolic clinic team will attend to your baby and provide a special formula or supplement to reduce their Phe levels to a safe level. With early diagnosis and treatment of PKU, your child can grow and develop normally, as long as they receive careful monitoring and a low-phenylalanine diet.
PKU Management and Treatment
Treatment consists of adhering to a life-long, low-protein diet. The level of protein intake from foods is based on the extent of the individual phenylalanine tolerance. To meet protein requirements, individuals need to take phenylalanine-free amino acid supplements enriched with micronutrients. Regular monitoring of phenylalanine levels involves collecting blood samples on a special card. The samples are sent to a laboratory and a metabolic dietitian will craft a detailed dietary plan. As your needs change, this plan can be adjusted. Early diagnosis and the proper diet and supplement treatment for PKU enable individuals to achieve their full potential.
The PKU Diet
The PKU diet is a diet for life, individuals with PKU cannot break down Phe in the usual way, so the amount of protein in their diet has to be restricted. NO meat, dairy, nuts/seeds, eggs, wheat, rice, grains, no meat substitutes, restricting vegetable and fruits. Food must be carefully weighed and protein content calculated to ensure the daily allowance is not exceeded. A special formula or supplement replaces the protein, vitamins and minerals that would normally be in their diet. Since the PKU diet limits protein intake, the supplement/formula compensates for what food does not provide. It helps keep Phe levels in the target range, provides all the essential amino acids (excluding or containing only small amounts of phe), tyrosine, vitamins, minerals and trace elements, and aids with fullness throughout the day. People with PKU obtain the other nutrients they need from food.
Other Potential Treatments
Sapropterin (Kuvan®) works as a co-factor which can help to improve the function of the phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme function enzyme (BH4) efficiency. Your state metabolic service will need to assess your suitability for Kuvan®. Only very few people with PKU are responsive to Kuvan®. This means that the majority of people with PKU will not show any response to Kuvan® and it will have no effects on their Phe levels. Kuvan® is listed on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) for use in Australia by all responsive PKU patients.
Pathways Support
MDDA offers IEM pathway support programs that provide information and resources to assist individuals in all aspects and stages of their PKU journey.
- Newly diagnosed
- Food starters
- Pre and school starters
- Tweens and transitioning adolescents
- Adults
- Maternal Women
- Return to care
- Carers for late diagnosed
Support Links & Materials
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Handbook
PKU Fruit Veg and Protein Counting Lists