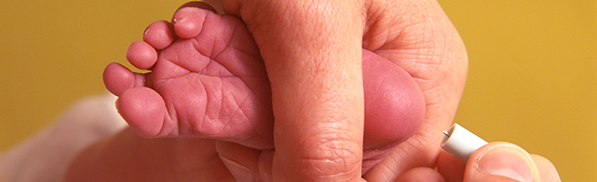
Every newborn baby in Australia is offered Newborn Bloodspot Screening (NBS), also known as the ‘Heel Prick Test”. It is a simple test to identify babies at risk of becoming seriously unwell from a rare condition. The newborn screening test is done in the first 48 to 72 hours after birth. This screening allows babies diagnosed with these rare conditions to receive the care and support earlier than they otherwise would.
Parents will often recall to us that they remember exactly where they were and what they were doing and how they felt when they received the call from the health specialist telling them their beautiful perfect baby has returned an abnormal test result.
Inborn Errors of Protein Metabolism (IEpM) represent the largest number of ‘screened for’ conditions in Australia with around 25-30 babies diagnosed each year. Early diagnosis and intervention ensure that babies receive the healthiest start to life possible. Most babies diagnosed with these conditions come from families with no previous history of these disorders.
In Australia, healthcare providers screen approximately 99% of babies every year. Of the babies screened, around 1 in every 1,000 has a condition that would otherwise have gone undetected.
How the Test is Done
Newborn Bloodspot Screening (NBS) is free for all babies in Australia. The midwife takes your baby’s sample by pricking your baby’s heel and collecting a few drops of blood on special filter paper. The NBS test is then sent to a specific laboratory and they perform tests to check for a range of serious conditions.
Results of the ‘heel prick test’ are available approximately 2 weeks after the test. You will receive contact only if your baby’s results are not normal. A specialist will then be recommended for further testing to diagnose your baby’s condition.
MDDA offers support to those families diagnosed with inborn errors of protein metabolism requiring life-long metabolic dietary management such as phenylketonuria.
History of Newborn Screening in Australia
Newborn Screening is one of the most successful public health programs in Australia. Phenylketonuria was first screened for in Australia in the 1960s.
In 1961 Dr Robert Guthrie from the USA developed a simple screening test of infants for phenylketonuria (PKU). Prospects for children with the disorder were poor before screening. Most children were not diagnosed in time to commence a low-phenylalanine diet, leading to irreversible brain damage and other health complications. Dr Guthrie went on to develop other bacterial inhibition tests which could be used to test for other marker metabolites of inborn errors of metabolism.
In the late 1990s the introduction of tandem mass spectrometry transformed newborn screening, allowing a single test to identify many conditions at the same time using the one blood sample. Newborn bloodspot screening in Australia spares thousands of children from intellectual and other disabilities and, in some cases, death. The technology related to the testing and management of conditions is quickly changing. Currently, Australia screens for over 25 conditions, and there are calls to incorporate additional conditions into the program.

Prevalence of IEpMs in Australia
Phenylketonuria (PKU) approximately 1:10,000, babies born in Australia
Arginase Deficiency (ARG) 1:350,000 to 1,000,000 births estimated worldwide
Argininosuccinic Acidemia (ASA) 1:70,000 to 1:218,000 births estimated worldwide.
Citrullinaemia approximately 1:100,000 births in Australia
Glutaric Acidaemia Type 1 (GA1) 1:100,000 births estimated worldwide
Homocystinuria (HCU) approximately 1:100,000 births in Australia
Isovaleric Aciduria (IVA) 1:250,000 births estimated worldwide.
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) approximately 1:100,000 births in Australia
Methylmalonic Aciduria (MMA) approximately 1:75,000 births in Australia
Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTC) 1:50,000 – 80,000 births estimated worldwide
Propionic Acidaemia (PA) 1:100,000 births estimated worldwide.
Tyrosinaemia Type 1 & 2 (TYRO) approximately 1:100,000 births in Australia
3-Methylcrotonyl CoA Carboxylase Deficiency (3MCC) 1:50,000 births estimated worldwide
NBS Resources
Monique’s (MDDA President) recalls Charlie’s newborn screening positive result
Department of Health NBS Website
‘For Katy’ a heartfelt family’s story who didn’t have access to NBS
